Alaska Blind Child Discovery
ATS-1 (Patch vs Atropine)
Home
PEDIG. A randomized trial of atropine vs. patching for treatment of moderate amblyopia in children. Arch Ophthalmol 2002;120(3):268-78.
OBJECTIVE: To compare patching and atropine as treatments for moderate amblyopia in children younger than 7 years. METHODS: In a randomized clinical trial, 419 children younger than 7 years with amblyopia and visual acuity in the range of 20/40 to 20/100 were assigned to receive either patching or atropine at 47 clinical sites. MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE: Visual acuity in the amblyopic eye and sound eye after 6 months. RESULTS: Visual acuity in the amblyopic eye improved in both groups (improvement from baseline to 6 months was 3.16 lines in the patching group and 2.84 lines in the atropine group). Improvement was initially faster in the patching group, but after 6 months, the difference in visual acuity between treatment groups was small and clinically inconsequential (mean difference at 6 months, 0.034 logMAR units; 95% confidence interval, 0.005-0.064 logMAR units). The 6-month acuity was 20/30 or better in the amblyopic eye and/or improved from baseline by 3 or more lines in 79% of the patching group and 74% of the atropine group. Both treatments were well tolerated, although atropine had a slightly higher degree of acceptability on a parental questionnaire. More patients in the atropine group than in the patching group had reduced acuity in the sound eye at 6 months, but this did not persist with further follow-up. CONCLUSION: Atropine and patching produce improvement of similar magnitude, and both are appropriate modalities for the initial treatment of moderate amblyopia in children aged 3 to less than 7 years.
PEDIG. The clinical profile of moderate amblyopia in children younger than 7 years. Arch Ophthalmol 2002;120(3):281-7.
OBJECTIVE: To describe the demographic and clinical characteristics of a cohort of children with moderate amblyopia participating in the Amblyopia Treatment Study 1, a randomized trial comparing atropine and patching. METHODS: The children enrolled were younger than 7 years and had strabismic, anisometropic, or combined strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia. Visual acuity, measured with a standardized testing protocol using single-surround HOTV optotypes, was 20/40 to 20/100 in the amblyopic eye, with an intereye acuity difference of 3 or more logMAR lines. There were 419 children enrolled, 409 of whom met these criteria and were included in the analyses. RESULTS: The mean age of the 409 children was 5.3 years. The cause of the amblyopia was strabismus in 38%, anisometropia in 37%, and both strabismus and anisometropia in 24%. The mean visual acuity of the amblyopic eyes (approximately 20/60) was similar among the strabismic, anisometropic, and combined groups (P =.24), but visual acuity of the sound eyes was worse in the strabismic group compared with the anisometropic group (P<.001). For the patients randomized into the patching group, 43% were initially treated for 6 hours per day, whereas 17% underwent full-time patching. Patients with poorer visual acuity in the amblyopic eye were prescribed more hours of patching than patients with better acuity (P =.003). CONCLUSIONS: In the Amblyopia Treatment Study 1, there were nearly equal proportions of patients with strabismic and anisometropic amblyopia. A similar level of visual impairment was found irrespective of the cause of amblyopia. There was considerable variation in treatment practices with regard to the number of hours of initial patching prescribed.
PEDIG, Holmes JM, Beck RW, Kraker RT, Cole SR, Repka MX, et al. Impact of patching and atropine treatment on the child and family in the amblyopia treatment study. Arch Ophthalmol 2003;121(11):1625-32.
OBJECTIVE: To assess the psychosocial impact on the child and family of patching and atropine as treatments for moderate amblyopia in children younger than 7 years. METHODS: In a randomized, controlled clinical trial, 419 children younger than 7 years with amblyopic eye visual acuity in the range of 20/40 to 20/100 were assigned to receive treatment with either patching or atropine at 47 clinical sites. After 5 weeks of treatment, a parental quality-of-life questionnaire was completed for 364 (87%) of the 419 patients.Main Outcome Measure Overall and subscale scores on the Amblyopia Treatment Index. RESULTS: High internal validity and reliability were demonstrated for the Amblyopia Treatment Index questionnaire. The overall Amblyopia Treatment Index scores and the 3 subscale scores were consistently higher (worse) in the patching group compared with the atropine-treated group (overall mean, 2.52 vs 2.02, P<.001; adverse effects of treatment: mean, 2.35 vs 2.11, P =.002; difficulty with compliance: mean, 2.46 vs 1.99, P<.001; and social stigma: mean, 3.09 vs 1.84, P<.001, respectively). CONCLUSION: Although the Amblyopia Treatment Index questionnaire results indicated that both atropine and patching treatments were well tolerated by the child and family, atropine received more favorable scores overall and on all 3 questionnaire subscales.
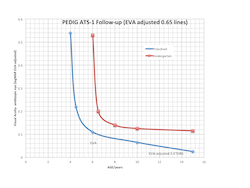
PEDIG, Repka MX, Wallace DK, Beck RW, Kraker RT, Birch EE, et al. Two-year follow-up of a 6-month randomized trial of atropine vs patching for treatment of moderate amblyopia in children. Arch Ophthalmol 2005;123(2):149-57.
OBJECTIVE: To compare patching and atropine sulfate as treatments for moderate amblyopia in children 18 months after completion of a 6-month randomized trial. METHODS: In a randomized, multicenter (47 sites) clinical trial, 419 children younger than 7 years with amblyopia (20/40 to 20/100 in the affected eye) were assigned to receive either patching or atropine eye drops for 6 months. Between 6 months and 2 years, treatment was at the discretion of the investigator.Main Outcome Measure Visual acuity in the amblyopic eye and sound eye after 2 years. RESULTS: At 2 years, visual acuity in the amblyopic eye improved from baseline a mean of 3.7 lines in the patching group and 3.6 lines in the atropine group. The difference in visual acuity between treatment groups was small: 0.01 logMAR (95% confidence interval, -0.02 to 0.04). In both treatment groups, the mean amblyopic eye acuity was approximately 20/32, 1.8 lines worse than the mean sound eye acuity, which was approximately 20/20. CONCLUSIONS: Atropine or patching for 6 months followed by best clinical care until 2 years produced similar improvement of moderate amblyopia in children between 3 and 7 years of age at enrollment. However, on average the amblyopic eye acuity was still approximately 2 lines worse than the sound eye.
PEDIG, Repka MX, Holmes JM, Melia BM, Beck RW, Gearinger MD, et al. The effect of amblyopia therapy on ocular alignment. J Aapos 2005;9(6):542-5.
PURPOSE: We sought to describe the change in ocular alignment at 2 years after treatment of amblyopia in children younger than 7 years of age at enrollment. METHODS: A randomized clinical trial of patching versus atropine for 6 months followed by standard clinical care for 18 months was conducted in 357 children with anisometropic, strabismic, or combined amblyopia (20/40-20/100) whose ages ranged from 3 to younger than 7 years at enrollment. Ocular alignment was evaluated at enrollment and after 2 years of follow-up. RESULTS: At enrollment when tested at distance fixation, 161 (45%) children were orthotropic, 91 (25%) had a microtropia (1-8 Delta), and 105 (29%) had a heterotropia >8 Delta. Of the 161 patients with no strabismus, similar proportions of patients initially assigned to the patching and atropine groups developed new strabismus by 2 years (18% vs. 16%, P = 0.84). Of these cases of new strabismus, only 2 patients in the patching group and 3 patients in the atropine group developed a deviation that was greater than 8 Delta. Microtropia at enrollment progressed to a deviation greater than 8 Delta with similar frequency in both treatment groups (13% vs. 15%, P = 1.00). Of the 105 patients with strabismus greater than 8 Delta at enrollment, 13% of those in the patching group and 16% of those in the atropine group improved to orthotropia without strabismus surgery. Strabismus surgery was performed in 32 patients during the 2-year study period. CONCLUSIONS: Patients who had amblyopia treatment with patching or atropine for 6 months followed by standard clinical care were found to have similar rates of deterioration and improvement of ocular alignment. When parents begin amblyopia treatment for children without strabismus, they should be warned of the possibility of development of strabismus, although it is most often a small angle deviation. Strabismus resolved after amblyopia therapy in some cases.
Repka MX, Kraker RT, Beck RW, Holmes JM, Cotter SA, Birch EE, et al. A randomized trial of atropine vs patching for treatment of moderate amblyopia: follow-up at age 10 years. Arch Ophthalmol 2008;126(8):1039-44.
ABCD History
Kids Eye Disorders
Amblyopia
Vision Screening
Issues
ABCD Clinics
References
Contact ABCD